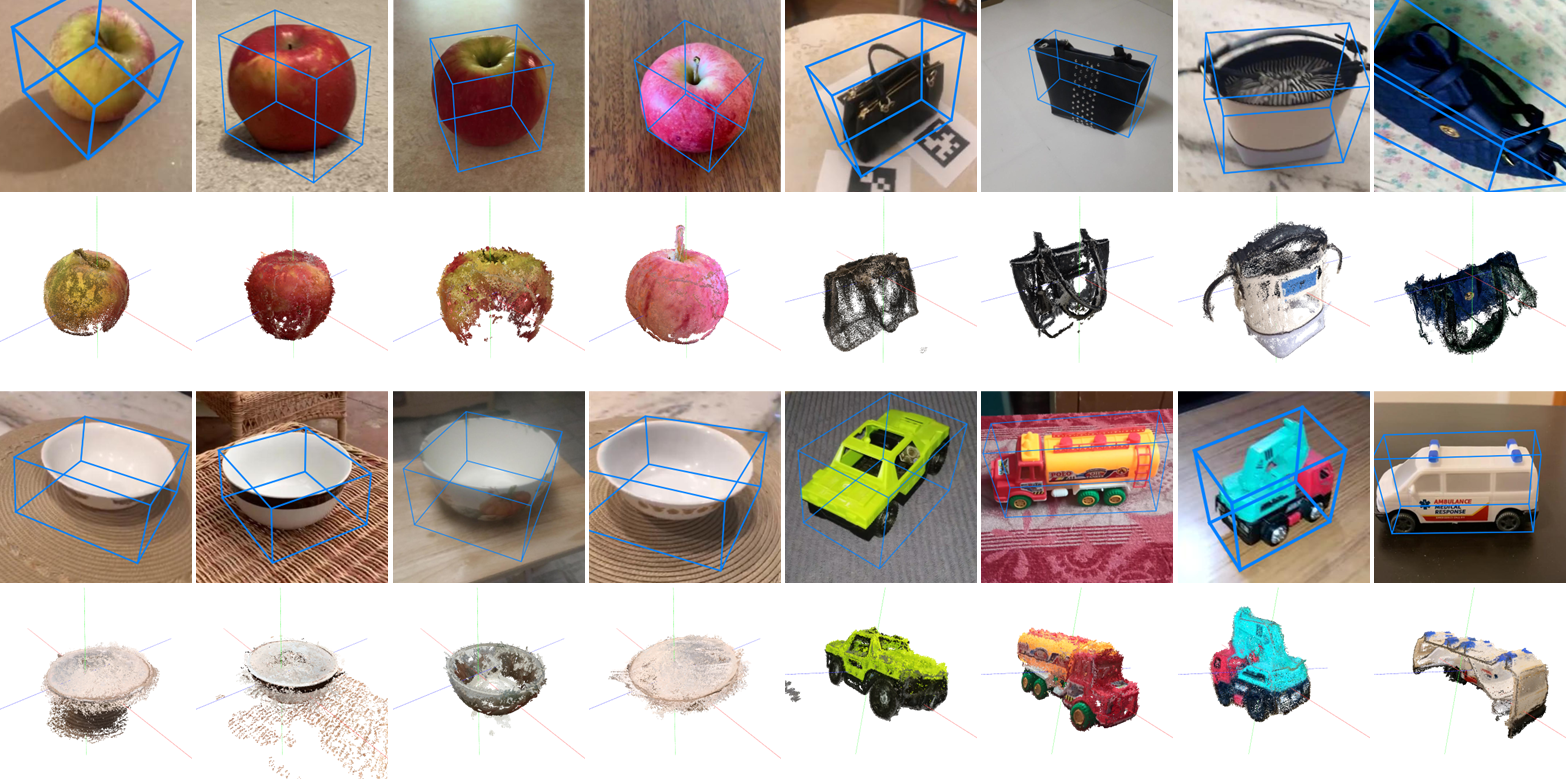
Dataset
Example images in OO3D-9D dataset. Single-object scenes as CO3D are displayed in the first row while challenging multi-object scenes are displayed in the second row.

This paper studies a new open-set problem, the open-vocabulary category-level object pose and size estimation. Given human text descriptions of arbitrary novel object categories, the robot agent seeks to predict the position, orientation, and size of the target object in the observed scene image. To enable such generalizability, we first introduce OO3D-9D, a large-scale photorealistic dataset for this task. Derived from OmniObject3D, OO3D-9D is the largest and most diverse dataset in the field of category-level object pose and size estimation. It includes additional annotations for the symmetry axis of each category, which help resolve symmetric ambiguity. Apart from the large-scale dataset, we find another key factor to enabling such generalizability is leveraging the strong prior knowledge in pre-trained visual-language foundation models. We then propose a framework built on pre-trained DinoV2 and text-to-image stable diffusion models to infer the normalized object coordinate space (NOCS) maps of the target instances. This framework fully leverages the visual semantic prior from DinoV2 and the aligned visual and language knowledge within the text-to-image diffusion model, which enables generalization to various text descriptions of novel categories. Comprehensive quantitative and qualitative experiments demonstrate that the proposed open-vocabulary method, trained on our large-scale synthesized data, significantly outperforms the baseline and can effectively generalize to real-world images of unseen categories.
Example images in OO3D-9D dataset. Single-object scenes as CO3D are displayed in the first row while challenging multi-object scenes are displayed in the second row.

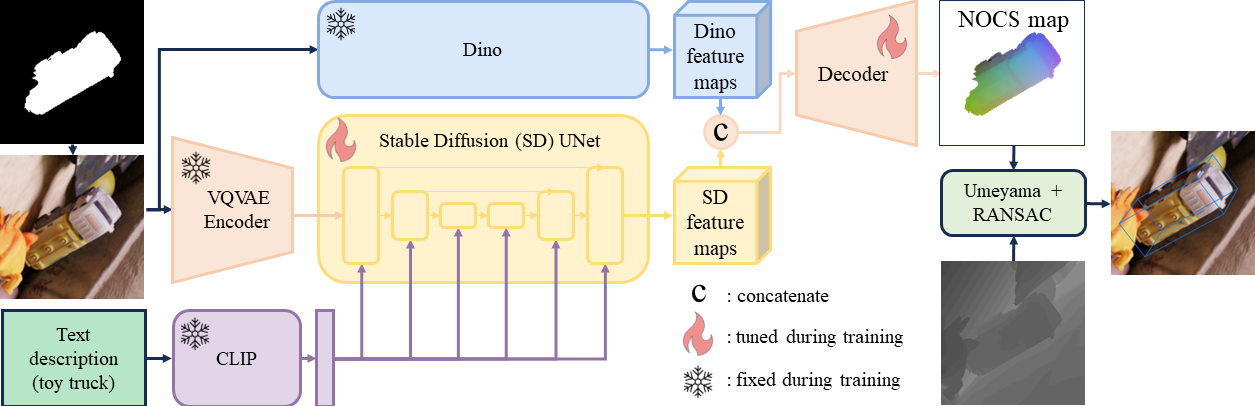
Overall framework. Text features are acquired from the prompt through the CLIP model and fed to the SD UNet. By combining these text features with latent visual features from VQVAE, SD feature maps are generated. Simultaneously, the DinoV2 module processes the masked RGB image to obtain Dino features. Both features are then combined in the decoder to estimate the NOCS map of the target object. During the inference stage, the depth map is utilized to establish correspondence between NOCS and the camera frame. Finally, the object's size and pose are computed using a pose-fitting algorithm.
Qualitative results on unseen real-world data. Our model trained with synthetic OO3D-9D data could directly perform 6D pose and size estimation on the unseen real-world Co3Dv2 dataset. The odd rows display cropped real-world images with our estimated 6D pose and size (visualized with the object bounding box), while the even rows display their corresponding aligned shapes in the normalized object coordinate space.
